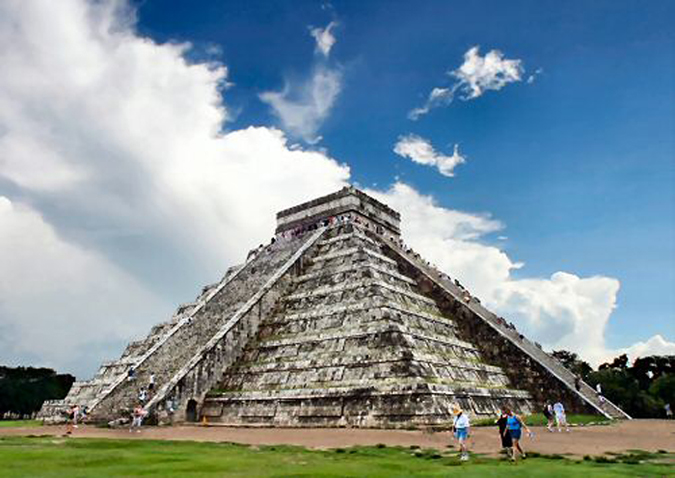
Climate
|
|
The Tropic of Cancer effectively divides the country into temperate and tropical zones. Land north of the twenty-fourth parallel experiences cooler temperatures during the winter months. South of the twenty-fourth parallel, temperatures are fairly constant year round and vary solely as a function of elevation. |
|
Areas south of the twenty-fourth parallel with elevations up to 1,000 meters (the southern parts of both coastal plains as well as the Yucatán Peninsula), have a yearly median temperature between 24 and 28 °C, or 75-82°F. Temperatures here remain high throughout the year, with only a 5 °C (41°F) difference between winter and summer median temperatures. Although low-lying areas north of the twentieth-fourth parallel are hot and humid during the summer, they generally have lower yearly temperature averages (from 20 to 24 °C/68-75°F) because of more moderate conditions during the winter. |
Many large cities in Mexico are located in the Valley of Mexico or in adjacent valleys with altitudes generally above 2,000 m, this gives them a year-round temperate climate with yearly temperature averages from 61-72°F and cool nighttime temperatures throughout the year. Many parts of Mexico, particularly the north have a dry climate with sporadic rainfall while parts of the tropical lowlands in the south average more than 200 cm of annual precipitation. |
|
|
| |
Geography |
|
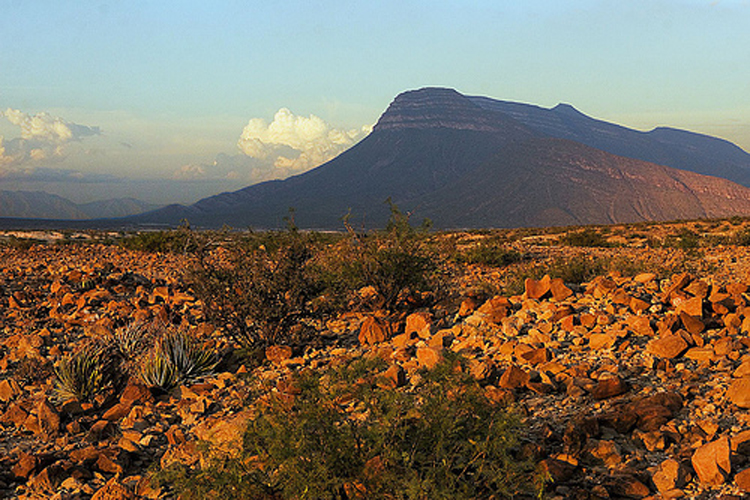
| Mexico is very diverse geographically. It is made up of fertile valley, tropical foresets, hight mountain peaks, deep canyons and desert landscapes. The northernmost portion of Mexico is covered by two different deserts. The largest is the Chihuahuan desert which covers approximately 176,700 sq mi (453,000 sq km) and is centered between the Sierra Madre Occidental and Sierra Madre Oriental mountain ranges. The Sonoran desert covers about 86,000 sq mi (221,000 sq km) and ranges from the majority of the Baja peninsula and the northwestern portion of the mainland.Northern and central Mexico have also have coastal plains on the east and west and two north/south mountain ranges framing a group of broad central plateaus known as the Altiplano Central. The Altiplano Central is divided into northern and central parts, themselves split by minor ranges and varies in altitude from about 3,300 ft (1,000 mt) in the north to more than 6,500 ft (2,000 mt) in the center of the country. The central plateau is mostly rolling hills and broad valleys and includes some of the best farm and ranch land in the country. The altiplano is bound on the east by the Sierra Madre Oriental and includes peaks as high as 12, 000 ft (3,700 mt). The Gulf Coast plain is an extension of a plain in the US and is wide in the north but narrows as it nears the port of Veracruz . |
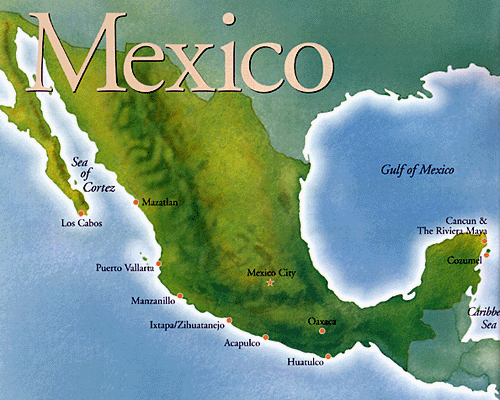
The Republic of Mexico’s 31 states and one federal district covers almost 780,000 square mi making it the world’s eight largest nation. The country curves from northwest to southeast, narrowing to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in the south and then continuing northeast to the Yucatan Peninsula . To the west and south it’s bordered by the Pacific Ocean . The Sea of Cortes lies between the mainland and Baja California , the world’s longest peninsula. Mexico ’s east coast is bordered by the Gulf of Mexico all the way from the US border to the northeastern tip of the Yucatan Peninsula . The eastern Peninsula faces the Caribbean Sea . |
 |
|
| South of the Altiplano Central and the two Sierra Madres, the Cordillera (mountain range) Neovolcanica runs east-west acress the country. This range includes the active volcanoes Popocatepetl (17, 800 ft; 5,452 mt) and Volcan de Fuego de Colima (13,000 ft; 3,960 mt), as well as Mexico’s other highest peaks, Pico de Orizaba (18,000 ft; 5,611 mt), Iztaccihuatl (17,300 ft; 5,286 mt) and Paricutin (9,200 ft; 2,800 mt). |
The Pacific lowlands cover a narrow strip west of Guadalajara . The Sierra Madre del Sur stretches across Guerrero and Oaxaca to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec the narrowest part of Mexico . The north side of the isthmus is part of a wide, marshy plain stretching from Veracruz to the Yucatan Peninsula . In the southernmost states the Pacific lowlands are backed by the Sierra Madre de Chiapas, the Rio de Grijalva basin and the Chiapas highlands. Each of these highlands is a tropical rainforest area stretching into northern Guatemala . The jungle turns into a region of tropical savanna on the flat, low Yucatan Peninsula and at the tip of the peninsula, an arid desert-like region. |
https://hearstmuseum.berkeley.edu/outreach/pdfs/mexican_folk_art.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mexico
https://www.questconnect.org/mexico_cc_geography_climate.htm
|



